
Why VO2 Max Testing Is Essential for Achieving Your Fitness Goals
Cardiovascular fitness, measured by VO2 max, is a crucial indicator of overall health and longevity. VO2 max represents your body's maximum oxygen consumption during physical exertion and serves as a reliable predictor of athletic performance and life expectancy.
Studies show that individuals with high fitness levels have a five-fold decrease in mortality rate compared to those with low fitness levels, with no upper limit to these benefits.
How to Test Your VO2 Max:
- Professional Testing:
- Cardiopulmonary exercise test at medical facilities
- Performance-based testing at specialized centers
- At-Home Testing Methods:
- Cooper Test: Run/walk for 12 minutes, calculate using formula (35.97 x miles) - 11.29
- 1.5 Mile Run Test: Complete distance and use time-based calculations
- Modified Bruce Protocol: Treadmill test with increasing intensity levels
Understanding VO2 Max Scores:
- Measured in milliliters per kilogram of body weight per minute
- One MET (metabolic equivalent) = 3.5 ml O2/kg/min
- Average 30-year-old should be above 35 ml range
- Elite athletes can score over 90 ml
Age-Related Considerations:
- After age 40, VO2 max declines by:
- 10% per decade for sedentary individuals
- 5% per decade for active individuals
Improving Your VO2 Max:
- Exercise at intensities above 60% of your VO2 max
- Optimal improvement occurs at 90% intensity
- Most effective training method: 4x4 intervals
- 4 minutes at 90% max heart rate
- 4 minutes active rest at 70% max heart rate
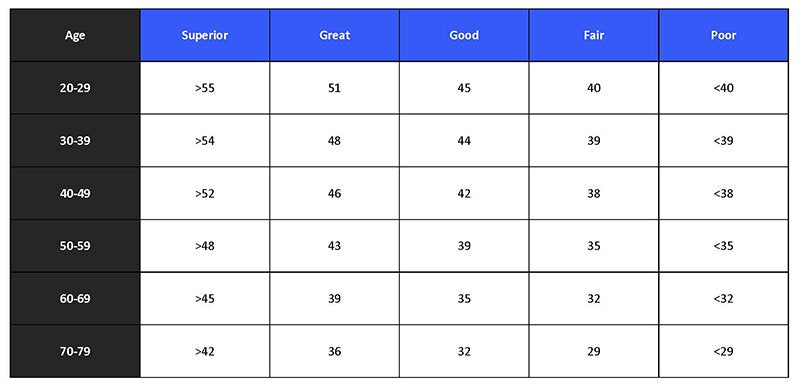
VO2 Max Fitness Level Chart
For optimal heart health and longevity, aim to elevate your heart rate above 60% at least weekly. Regular cardiovascular training, especially high-intensity interval training, can significantly improve your VO2 max and overall health outcomes.
Setting long-term fitness goals, such as maintaining ability to climb stairs or run distances in later years, can help guide your current fitness targets and ensure healthy aging.
Related Articles

Cannabis Use Linked to 6 Times Higher Risk of Heart Attack in New Studies

