The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Healthiest Milk for Your Needs
Milk Types: A Comprehensive Nutritional Comparison

Glass bottle of almond milk
The most common milk types available today include cow's milk, soy milk, oat milk, almond milk, hemp milk, rice milk, and coconut milk. Each offers unique nutritional benefits and suits different dietary needs.
Milk types comparison chart
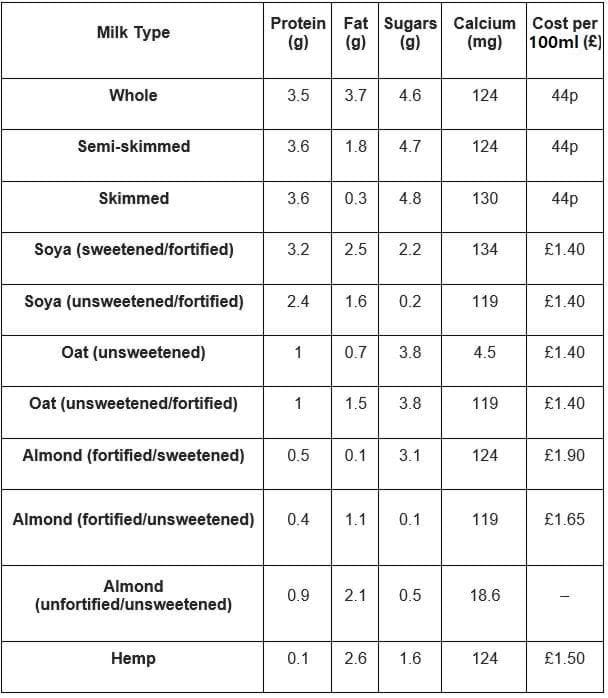
Cow's Milk (per 100ml)
- Calories: 47
- Fat: 1.8g
- Protein: 3.6g
- Sugars: 4.7g
- Benefits: High in calcium and protein, rich in amino acids
- Drawbacks: Contains lactose, higher in calories, may contain antibiotics (non-organic)
- Cost: Most economical option
Soy Milk (per 100ml)
- Calories: 39
- Fat: 1.6g
- Protein: 2.4g
- Sugars: 0.2g
- Benefits: Similar to semi-skimmed milk, rich in calcium and protein
- Drawbacks: Contains phytic acid, which may affect mineral absorption
Oat Milk (per 100ml)
- Calories: 42
- Fat: 0.7g
- Protein: 1g
- Sugars: 3.8g
- Benefits: Allergen-free, fortified with vitamins D, iron, calcium
- Drawbacks: Lower protein content
Almond Milk (per 100ml)
- Calories: 22
- Fat: 1.1g
- Protein: 0.4g
- Sugars: 0.1g
- Benefits: Low-calorie, high in vitamin E, highest calcium among nut milks
- Drawbacks: Low protein content
Hemp Milk (per 100ml)
- Calories: 21
- Fat: 2.6g
- Protein: 0.1g
- Sugars: 1.6g
- Benefits: Rich in amino acids and omega-3
- Drawbacks: Lower calcium content, more expensive
Choosing the Right Milk: Consider your dietary needs, nutritional goals, and taste preferences. If you get sufficient nutrients from other sources, choose based on taste. Otherwise, select a milk that complements your nutritional needs.

image

Woman strength training on treadmill

Woman exercising with weights
