
Essential Facts About Deadly Traveling Blood Clots: Symptoms and Risks
A blood clot that forms in a deep vein (DVT) can become life-threatening if it breaks off and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism (PE). Understanding the risks and symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment.
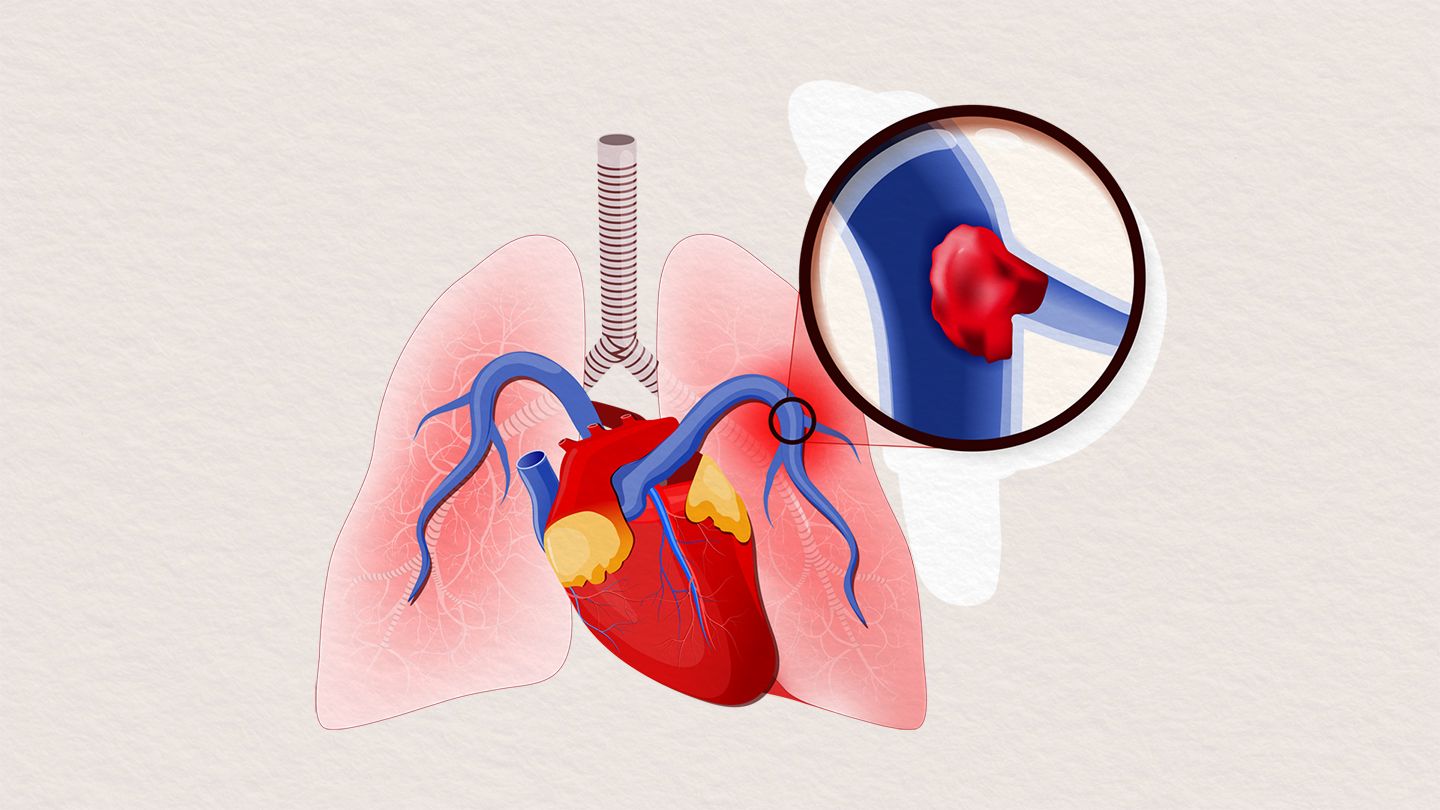
Blood clot forming inside heart
Common DVT Symptoms:
- Swelling in one arm or leg
- Unexplained tenderness
- Warm, red skin in the affected area
- Usually affects only one limb
Pulmonary Embolism Warning Signs:
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid heartbeat
- Chest pain (worse when breathing deeply)
- Coughing up blood
- Lightheadedness
- Anxiety or sweating
- Fever
- Clammy or discolored skin
Major Risk Factors:
- Extended periods of sitting (long travel)
- Hormone therapy or pregnancy
- Recent surgery or hospitalization
- Being overweight
- Age over 55
- Smoking
- History of blood clots
- COVID-19 infection
- Chronic health conditions
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- DVT: Usually diagnosed through duplex ultrasound
- PE: Detected using CT scans or specialized lung X-rays
- Treatment typically involves blood thinners
- Severe cases may require clot-dissolving medications or surgery
When to Seek Emergency Care: Immediate medical attention is necessary if you experience:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Severe chest pain
- Coughing up blood
- Signs of DVT with risk factors present
Prevention is critical, as up to 100,000 Americans die annually from DVT and PE complications. Never ignore potential symptoms, especially if you have risk factors. Early detection and treatment significantly improve outcomes.
Related Articles
12 Early Warning Signs of Diabetes: Essential Symptoms to Never Ignore

