A Complete Guide: Which Type of Milk is Best for Your Health?
Plant and animal-based milks each offer unique nutritional benefits. Here's a comprehensive comparison to help you choose the best option for your needs:

Glass of milk beside almond nuts
Common Types of Milk:
- Cow's milk
- Soy milk
- Oat milk
- Almond milk
- Hemp milk
- Rice milk
- Coconut milk
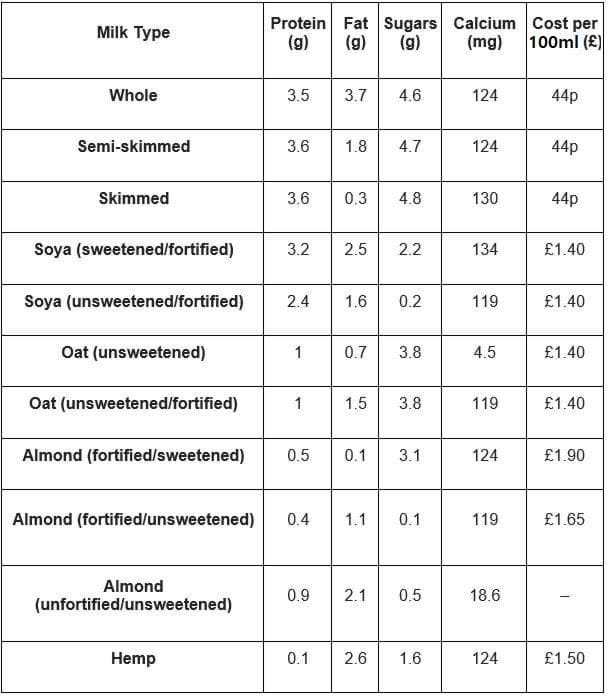
Milk nutrition comparison table
Cow's Milk (per 100ml):
- Calories: 47
- Fat: 1.8g
- Protein: 3.6g
- Sugars: 4.7g
- Benefits: High in calcium and protein, rich in amino acids
- Drawbacks: Contains lactose, higher in calories, may contain antibiotics if non-organic
Soy Milk (per 100ml):
- Calories: 39
- Fat: 1.6g
- Protein: 2.4g
- Sugars: 0.2g
- Benefits: Similar to semi-skimmed milk, high in protein and calcium
- Drawbacks: Contains phytic acid which may affect mineral absorption
Oat Milk (per 100ml):
- Calories: 42
- Fat: 0.7g
- Protein: 1g
- Sugars: 3.8g
- Benefits: Allergen-free, fortified with vitamins and minerals
- Drawbacks: Lower protein content
Almond Milk (per 100ml):
- Calories: 22
- Fat: 1.1g
- Protein: 0.4g
- Sugars: 0.1g
- Benefits: Low calories, high in vitamin E, highest calcium among nut milks
- Drawbacks: Low protein content
Hemp Milk (per 100ml):
- Calories: 21
- Fat: 2.6g
- Protein: 0.1g
- Sugars: 1.6g
- Benefits: Rich in amino acids and omega-3
- Drawbacks: Lower calcium content, more expensive
Choosing the Right Milk: Consider your dietary needs, nutritional goals, and personal preferences when selecting milk. Factor in:
- Calcium requirements
- Protein needs
- Lactose tolerance
- Caloric goals
- Dietary restrictions
- Cost considerations

image

Woman strength training on treadmill

Woman exercising with weights
